"Topical Negative Pressure (Vacuum-Assisted Closure VAC)"
It is a non-invasive method that provides controlled and localized negative pressure application on the wound in order to accelerate healing in acute and chronic wounds. It is a treatment method based on closing the wound area in a sterile manner and applying negative pressure (suction) continuously or intermittently (pulsed).
In this technique, special sponges are used to fill the gaps in the wound, adhesive semi-permeable caps to close the wound, a device that connects the device to the wound and regulates the pressure (T.R.A.C. Pad, Therapeutic Regulated Accurate Care), a collector container (canister/infiltration container) and negative pressure. (CareOxi Consumables General) It consists of a device that creates A small hole is made in the cover, a TRAC pad is placed and a VAC device is connected to the wound. It is operated continuously at 100-150 mmHg for 48 hours and then intermittently. The dressing is changed every 48-72 hours.
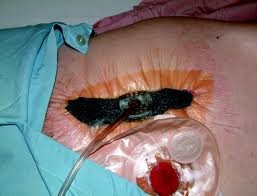
This method is a treatment method that helps healing in difficult wounds, slow healing and recurrent wounds. With vacuum therapy, wound healing is accelerated by applying a certain negative pressure to the wound. It has a positive effect on the development of granulation tissue by increasing local blood flow by approximately 4 times, especially in chronic or traumatic wounds with limited blood flow, and with this effect, it accelerates the development of wound healing tissue, that is, "granulation tissue", while reducing the number of bacteria. In addition, by pulling the wound created by the system centripedally with mechanical stress, wound contraction and a significant reduction in wound size are achieved. In addition, edema, which is an important problem especially in subacute wounds, and the harmful effects of this edema are minimized as a result of the system reducing the edema fluid with the vacuum effect.
Continuous negative pressure application has a positive effect on the wound. Wound care with the application of negative pressure is promising, especially in chronic, problematic and difficult-to-heal wounds.
An important point that should not be forgotten when evaluating the effects of the vacuum system is that in order for the system to be effective, it must be applied to living tissues that have blood flow. What no system developed to date has been able to do, and most likely will not be able to do, is the revitalization of dead tissue. Therefore, it is clear that the appropriate treatment should be done on wounds whose necrotic tissues have been debrided and under the supervision of people trained and experienced in wound care. It does not need to be applied to wounds with normal wound healing, but it can be used in wounds that heal slowly and have become chronic, when the above conditions are met.
Wet and dry wound dressings, repeated twice a day, are the most commonly used methods for open wounds. Hyperbaric oxygen treatments, another adjunctive treatment method, give good results in cases where oxygenation is limited. In addition, ready-made wound dressing materials from various companies available in the market also contribute to wound healing when used at the right time and place.
In vacuum therapy, an aspiration device that creates subatmospheric pressure is needed to diffusely apply negative pressure to the wound in a controlled closed environment. Sterile polyvinyl sponge is used to distribute the pressure on the wound as effectively as possible. Sterile surgical drape is a suitable material that can be used to create a closed environment. After cleaning the wound under sterile conditions, a size 20 nasogastric tube (NGT) is passed through a medium-soft polyvinyl sponge prepared in accordance with the wound dimensions and ideally approximately 1 cm larger than the wound dimensions. Then, the top and surroundings of the sponge are carefully covered with a sterile surgical drape, preventing air intake, and the free end of the NGT is connected to a continuous aspirator device that can produce 120 mmHg subatmospheric pressure. This application can be kept in place for 3 to 5 days, depending on the secretion status of the wound, and can be reapplied in the same way if necessary.
This method has a positive effect on the development of granulation tissue by increasing local blood flow approximately 4 times, especially in chronic or traumatic wounds with limited blood flow, and accelerates granulation development by reducing its number. By pulling the wound created by the system centripedally with mechanical stress, wound contraction and a significant reduction in wound size can be achieved. In addition, as a result of the reduction of edema, which is an important problem especially in subacute wounds, with the vacuum effect, the harmful effects of edema are reduced to a minimum.
In addition to its positive effects on wound healing, which have been shown experimentally and supported by clinical studies, the reduction in the number of dressings is important in two ways:
Wound care with the application of negative pressure is promising, especially in chronic, problematic and difficult-to-heal wounds.
Vacuum therapy units and oxygen therapy units are available separately today for the treatment of open wounds. With the closure sets that are closed and adhered to the wound, the pus and bacteria on the wound are removed by vacuum units. Afterwards, oxygen is given to the cleaned wound for treatment purposes with oxygen therapy units.
Having the units separately creates problems both in terms of usage and economy.
Wound repair is one of the cornerstones of plastic surgery. The purpose of wound care is to keep the wound clean until the planned surgery and to increase the chances of success of the treatment by ensuring the development of healthy granulation tissue. Direct reconstruction is often not possible due to the patient's condition or the size of the wound. After evaluating the condition of the wound, surgical debridement (removal of the dead layer) is performed to remove infected bacteria, foreign materials and necrotic tissue from the wound.
The next treatment is to continue wound care until the wound appears healthy and vascularized. The selection of products used in this process depends on the experience of doctors and nurses and their ability to start trying new possibilities.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) CareOxi Device Usage Areas
All Hospitals; Acute and Chronic Wound Care Clinics, Burn Treatment Centers, Diabetic Patient Treatment Centers, Intensive Care Centers, Palliative Care Centers, Orthopedic Clinics, General Surgery Clinics, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Clinics, Geriatric Patient Clinics, Home Health Units, etc.
CareOxi consists of a unit developed for applying vacuum to be used in the treatment of burn wounds and all kinds of open wounds, and a closure set for treating open wounds. The vacuum-only version of the system is called CareOxi HandyVac.
CareOxi consumables, which are used with the device and are specially designed to provide negative pressure on the wound and also to use the application features of the CareOxi device, are a part of the system. On CareOxi Consumables; There is a special adhesive section that allows adhesion to the wound area and is integrated with the consumable or separate (medical film/drap). For the operating effectiveness of the CareOxi device; On the floor of the CareOxi consumable, which has outlets where the exudate and medicated wash on the wound are vacuumed; It includes folding so that positive and negative pressure can function simultaneously, and a pocket layer so that physicians can properly place sponges or cloths that have a sponge/moisturizing healing-accelerating feature.
The device has a chamber (exude container) where the pus, bacteria and small dead skin particles sucked from the wound with the help of vacuum are collected. A Hepa filter is placed at the hopper outlet. The check valve inside the chamber prevents the collected pus, bacteria and dead skin particles from flowing back.
The closures used (medical grade foam) are hydrophobic materials used in medicine and can be covered with a transparent film in an airtight manner and are compatible with device apparatus. The material has a microdeformation effect and this feature is supported by clinical publications. The material is microporous, has high elasticity and has increased density.
While negative pressure is applied, the set does not damage the capillaries, granulation tissue and epithelium and keeps the pain threshold very low. Blood flow is provided in the capillaries with the periodic vacuum system. Treatment is accelerated by transporting O2 to the tissues. Material covering the wound in the set; It can be produced as standard and impregnated with polyvinyl alcohol, antibiotics or paraffin. Silver ion impregnated types are also available.
Foam dressing materials and their properties that can be used in the Vacuum Assisted Closure System: In general, they are hydrophobic (water repellent), allowing high vacuum drainage, and providing homogeneous distribution of negative pressure on the wound. It allows closure by filling the wound space in heavily exuding, infected and cavitated wounds.
The surface area of the sponge varies depending on the size of the covering set.:
Small: ...
Medium: ...
Big: It can be cut to 324 cm2
or desired dimensions.
Exudate-attracting sponges, used independently of the VAC device, are applied according to physician control and wound level. These;
Vacuum-assisted collection sets of different volumes suitable for the CareOxi system allow appropriate selection for wounds with different wound drainage and exudate capacity. The one-piece structure of collection sets ensures safe storage of effluent throughout treatment. While the integrated filter system in the collection set prevents liquid passage into the device, it prevents the odor from spreading to the outside environment with the special chemical component (gel) in the chamber. In addition, the solidifying gel contained in each collection set increases environmental safety by preventing the movement of the collected waste liquid. Since the collection sets are integrated with the vacuum device, the vacuum device does not prevent the patient from moving even when it is in the carrying bag. Luer-lock spout provides easy and secure connection with closure on the wound.
The collection container is compatible with the vacuum-assisted closing device (VAC) and does not prevent the device from giving an alarm in case of a change in the pressure applied during the treatment. There is a filter at the connection point to the device that prevents odor, bacteria and liquid from passing out of the container.
The collection container is non-openable, disposable, and has a feature that prevents the liquid collected in it from moving by gelling it. It has connectors compatible with the hose coming from the closing device and set. It is in sterile, single packages. There are signs on the canister that indicate volume.
There is a one-way valve or hydrophobic filter that prevents backflow at the entrance of the liquid aspirated from the patient to the exudate container. When the bag is full, the flow is cut off.
The exudate container is made of elastomer PVC, which is resistant to falling and breaking.
The device is a whole with the wound closure set and collection set, which are used together in an integrated manner. The wound closure set and collection set (collection container) are disposable and are disposed of as medical waste after use.
Thanks to its unique silicone structure, it provides the gentlest interface for the patient. With its useful design, it can be easily applied to the sponge dressings on the wound, making it easier to start vacuum-assisted treatment. TRAC Pad, which consists of suction cup, adhesion tape, connection hose, clamp and connector for device connection, is disposable and its usage period is; until the vacuum wound closure set is removed from the patient.
To apply it on wound closure, all that needs to be done is to remove the protective paper on the back of the port and stick it on the drape covering the wound. With its biocompatible silicone dome and silicone hose, it provides sensitive touch as well as higher resistance to bending and breaking. It ensures safe and easy connection with the Luer-lock / snap-on spout collection set.
It consists of a connection hose, drape (transfer adhesive film) and suction cup. The suction cup is soft and is connected to the VAC device by placing it in the hole opened on the vacuum wound closure. The suction cup and the connection tube are glued together with special medical adhesive, and drape is added to adhere to the wound. A cutting mechanism (compressor, wrench, etc.) is located on the Trac pad to prevent leakage from the vacuum area on the Trac pad (when the vac device is off). The places where the Trac pad is connected to the VAC device are of a special plug-in type compatible with the device. It is disposable.
Barrier film / tape (Drep / Drape), which is a part of the vacuum-assisted closure set, is used to create a barrier to exposed organs and to ensure that the closure sponge remains stable in the area where it is placed. There are holes on the drape, which is a barrier, to make drainage connections or they are opened after the appropriate wrapping process. The general feature of drape is that it is transparent, sterile and airtight.
Transparent protective film; Polyurethane is bacteria and waterproof and hypoallergenic. Can be sterilized with Ethylene Oxide.
